Getting Started
Step 1
Schedule an Introductory Consultation
Step 2
Schedule a QEEG (BrainMap)
Step 3
QEEG (BrainMap) Analysis
Step 4
Begin Neurofeedback Therapy
How We Collect & Learn From Brainwaves
How do I start with neurofeedback?
A comprehensive assessment is where neurofeedback therapy begins. The assessment allows doctors to determine whether a client’s brainwave patterns are different from normal. Based on your brain map results, we then create a restorative plan of care. Each assessment provides the doctor with neurofeedback training protocols. These protocols are designed to retrain the brainwave patterns towards normal. The result of rebalancing these brain waves restores health, healing and functionality for lasting results.
Read Your Mind
During neurofeedback sessions, doctors are actually able to identify abnormal brainwaves.
-
Which Frequency Band & Areas of the Brain to Train
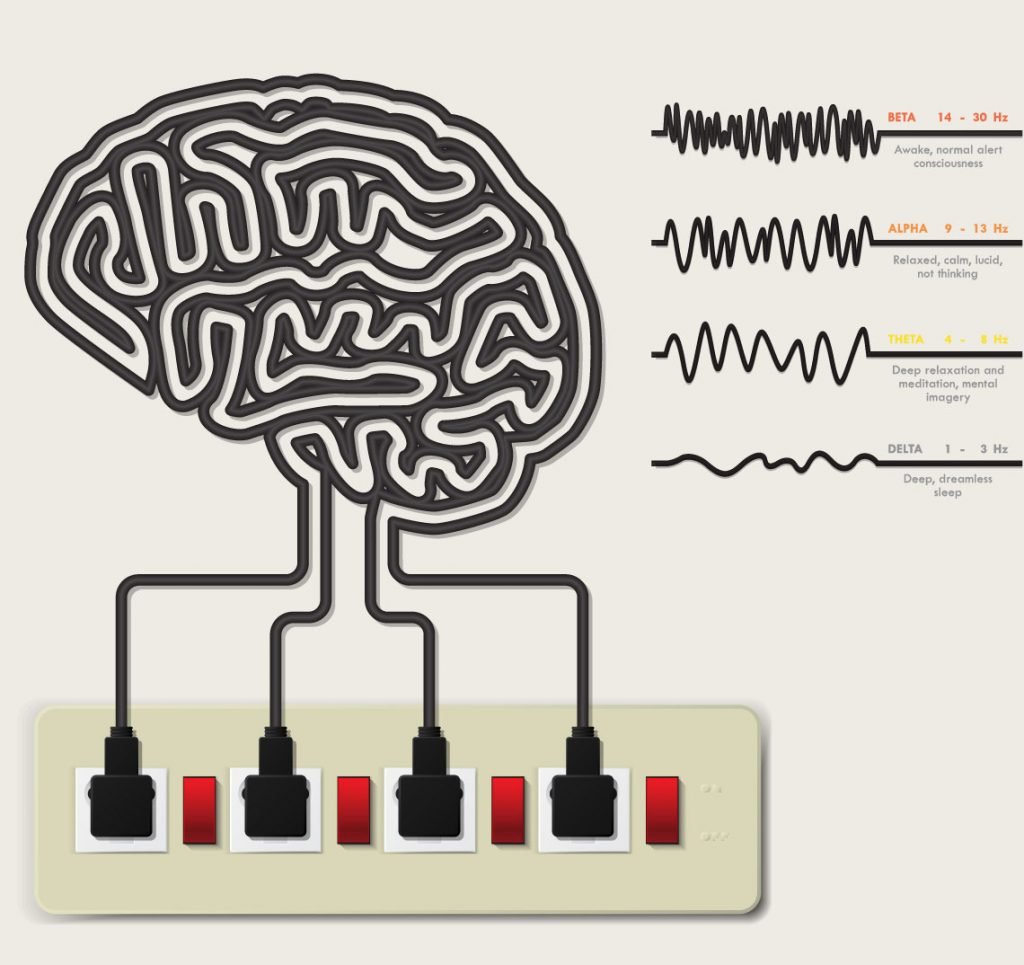
The qEEG-report is the assessment process that allows us to determine the brain wave patterns by gathering information about the electrical activity of specific locations of the brain. To do this, we place what looks like a swim cap with a number of sensors on your head to measure the brain wave activity of the various frequency bands. This is done with the client sitting quietly with his or her eyes closed for approximately 5 minutes and then with eyes open for an additional 5 minutes. Our equipment will then analyze this information and generate a series of images that will identify which areas of the brain may be too active or not active enough. This is called a Brain Map. The Brain Map provides an invaluable overview of what is going on in the brain and will be used in conjunction with information provided by the client to develop the training plan.
-
How is Neurofeedback Done?
Sensors are placed on the head and ears to record the brainwave activity. High-tech equipment amplifies the electrical impulses and breaks them into the four key frequency bands. Using sophisticated computer software a customized protocol is developed to address the individual’s unique needs. During the session the Neurofeedback Clinician views the raw EEG signal as well as the chosen frequency bands. Exercises can be done with either eyes open or eyes closed. With eyes open the Client is watching a video or playing a game. The video fades in and out depending on whether or not the brain is increasing the desired.
-
Why Does Neurofeedback Work?
Neurofeedback takes advantage of the brain’s ability to change itself through a process known as Neuroplasticity. It utilizes the same learning process that occurs whenever we acquire a new skill. The brain learns by forming connections between nerve cells and utilizing important pathways that connect different locations in the brain. The more frequently you utilize these pathways the better the brain becomes at performing the associated task. In psychology, this type of leaning is called “Operant Conditioning”. It is a type of learning in which responses come to be controlled by their consequences. Quite simply, Neurofeedback offers the perfect learning conditions, since it facilitates awareness of when the brain is producing healthier brainwave patterns, provides reinforcement for the positive change and multiple opportunities to provide practice during a training session.
Understand Your Brain
Understand the symptoms that may be associated with specific brainwave imbalances.
Delta/Theta Imbalance
Cognitive Impairment
Impulsivity
Hyperactivity
Focus and Attention Issues
ADHD
Socially Inappropriate
Easily distracted
Excessive Speech
Disorganized
Hyper-emotional
Traumatic Brain Injury
Dementia
Learning Disorders
Autism / Asperger’s
Alpha Imbalance
Depression
Victim Mentality
Excessive Self Concern
Passive Aggressive
Irritability
Avoidance Behavior
Rumination
Anger
Self-Deprecation
Agitation
Fibromyalgia
Withdrawal Behavior
Beta Imbalance
Anxiety
OCD
Migraine
Tension Headaches
Insomnia
Obsessive Thinking
Excessive Rationalization
Poor Emotional Self-awareness
Panic Attacks
Worry
Chronic Pain
Hyper-vigilant
Dislike Change
Restless